How To Secure RDP: Best Practices for Protecting Your Remote Desktop
RDP has developed into an essential tool in today’s digitally driven world. It provides access to a computer from another location, allowing it to be controlled. This puts IT administrators in a place where they can easily administer servers, while employees can access work computers from anywhere in the world. This convenience, however, comes with big security risks brought in by RDP. There are cases of unauthorized access and cyber-attacks targeting RDP; hence, securing RDP connections is not something to be taken lightly. This guide walks you through the best practices to secure your remote desktop and guarantee the integrity of data and systems.
Introduction to Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)
RDP is a proprietary protocol developed by Microsoft that allows one to connect to another computer by network address. Thus, RDP grants access to and control over a remote machine as if the user were seated personally at it. This functionality comes especially in handy for IT administrators in management cases when the server is located remotely or employees need to work from home. Through RDP, this fluid and responsive user experience is achieved by continuously sending screen data from the client device to the remote host while simultaneously streaming the keyboard inputs and mouse movements back to the remote host.
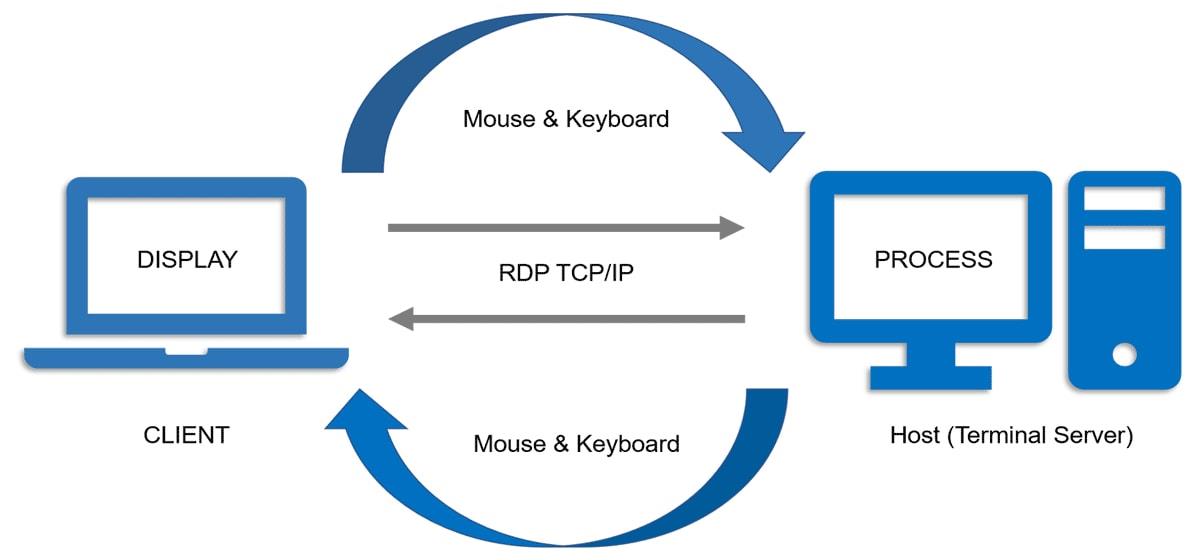
What is RDP, and why is it important?
Remote Desktop Protocol is developed by Microsoft and provides access to a remote computer desktop, facilitating IT management, remote work, and technical support. It offers greater productivity and flexibility for both remote workers and IT administrators, yet it also opens up security risks. With its wide adoption in the usage and storage of sensitive data, RDP is very often targeted by cybercriminals. The security of RDP is, therefore, indispensable in helping to deter unauthorized access, data leakage, and other pernicious activities; the best practices will be very imperative in safeguarding the system and data.
Best Practices for Securing RDP
RDP needs to be secured against unauthorized access and cyber-attacks. Best practices are methods to keep your RDP connections safe and secure. Some of those are strong passwords, two-factor authentication, network-level authentication, access restriction through firewalls, changing the default ports, and virtual private network usage. These best practices will largely help you in making your remote desktop setup much more secure and systems safe from any potential threats.
Use strong passwords and two-factor authentication
First of all, one has to set strong and unique passwords. The activation of 2FA to secure RDP should follow this. A strong password will contain both uppercase and lowercase letters. It also includes numbers and special characters. Avoid very common words and easily guessable information, but create complex passphrases. 2FA provides that additional layer of protection that, coupled with your password, requires another means of verification—like a code sent to your cell phone—to allow access in case your password has ever been compromised. Tools like Microsoft Authenticator can be utilized to turn on 2FA for additional RDP security.

Enable Network Level Authentication (NLA)
Network Level Authentication with RDP enhances security by providing the requirement for users to authenticate before starting a full session. This will help prevent unauthorized access and decrease denial-of-service attacks. To turn on NLA, go to the Remote tab within the System Properties of the remote machine and check the “Allow connections only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication” box. This simple step guarantees that only authenticated users will be connected, providing an essential layer of protection for your RDP setup.
Limit access to RDP and configure firewalls
One major importance of RDP setup is locking it down for security. IP whitelisting is a process that ensures a restriction to selected trusted IP addresses, hence avoiding possible unauthorized access to the server. Firewall rules track and manage the traffic out of RDP to make sure that only those authorized may connect to it. Firewalls act to prevent an attacker from exploiting vulnerabilities within the system. Review and update firewall rules regularly in light of changes to the network. They significantly minimize the risk of unauthorized access to your remote desktop sessions.
Change the Default RDP Port and Use VPNs
By default, RDP listens on port 3389—the same port attacked by default. Obscurity can be added, and automated attacks reduced by changing this to some other port. This may either be manipulated through editing of the Windows Registry or by Group Policy settings, ensuring that it is not too common, a new port used for the task. Security is hugely enhanced with a VPN used in conjunction with RDP because the former creates an encrypted tunnel for RDP traffic, which is very hard to intercept. Connecting to a VPN before starting the RDP session protects data transmission and anonymizes network traffic, hence providing strong protection for remote desktop connections.

Additional Safety Measures
Some complementary measures will help increase the security of Remote Desktop Protocol connections. It’s some of the best practices to protect your systems against unauthorized access and other cyber threats. Keeping the software updated regularly, monitoring your systems, having enforced policies of account lockout, configuring settings related to session timeout, and not allowing clipboard redirection but maintaining audit logs, make up for a robust security environment around your RDP connections.
Keep software updated, and regular monitoring
Keeping software up to date is critical in RDP security; generally, updates include patches for vulnerabilities that attackers can use. Keeping your operating system and RDP software updated will decrease these risks. It is also important to monitor the RDP connections to keep a tab on them so that detection of suspicious activity and reaction to it may be possible. Configure alerts on abnormal login attempts or access from unknown IP addresses, and analyze the logs and traffic to be able to identify at an early stage any possible security incidents and take remedial actions before they escalate into large problems.
Account Lockout Policies and Session Timeout Settings
Account lockout policies let one effectively secure RDP connections due to account lockout after a certain number of failed login attempts, hence balancing security and usability. Further, the timeout settings of the sessions are capable of reducing risks of unauthorized access by automatically logging off inactive sessions after a set period, say 30 minutes. By enforcing these two policies, you will have very secure RDP sessions by reducing the chances through which unauthorized access can be gained.
Disable Clipboard Redirection and Audit Logs
Clipboard redirection off—turning this off improves RDP security by not allowing the transfer of data from a local to a remote machine and vice versa. This feature can be turned off for further protection with the use of Group Policy settings. It is equally very important to keep audit logs and check them regularly for RDP activities. Audit logs record all login attempts and other significant actions; thus, they help in the detection of suspicious behaviour and unauthorized access. It sets up automated alerts for abnormal activities to enhance security. You will be able to monitor audit logs regularly, thereby quickly detecting and responding to security incidents to ensure the integrity of your RDP environment.
Conclusion
RDP security is essential in protecting against unauthorized system access and cyber-attacks. RDP enables remote computer control; hence, it is crucial to understand the type of security it needs. This best practice document will cover the use of strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication and network-level authentication, restricting access using firewalls, changing default ports, and finally, using a VPN. Besides, up-to-date software, monitoring of activity, enforcement of the account lockout policy, setting time outs for sessions, and disabling clipboard redirection strengthen security. Quick action, investigation, and hardening of security measures in case of a breach from the steps. Following these steps will help keep your RDP connections safe from any potential threats.







