VDI and RDP vs RDS: Understanding Remote Desktop Solutions
Remote desktop technologies, including Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI), Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), and Remote Desktop Services (RDS), are essential for enabling remote access to work environments. While all three systems allow users to access desktops or applications from any location, they differ in their implementation, features, and overall user experience. This blog post compares these solutions to help businesses and individuals choose the best one based on their specific needs. Customization, cost, and simplicity will be key to making an informed decision.
Contents
What is VDI?
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) enables users to access virtual desktops hosted on centralized servers, providing a full desktop experience. Each user has a dedicated virtual machine (VM) that is customizable and secure. VDI enhances data security by isolating users and is ideal for remote work, allowing access from anywhere with internet connectivity. A connection broker manages user sessions, ensuring efficient resource allocation and performance. Centralized processing and data storage increase security by keeping sensitive information within the protected data center.
Benefits of Using VDI
- Enhances security by isolating each user’s desktop environment.
- Prevents the spread of malware or security threats across other desktops.
- Allows administrators to control the desktop environment centrally.
- Enables the ability to push updates and centrally manage security settings.
- Supports flexibility and scalability, making it easy to add more virtual desktops as the organization grows.
- Does not require additional physical hardware for expansion.
- Simplifies management of a large number of users.
- Provides a consistent and customizable user experience.
- Compatible with multiple devices such as PCs, tablets, and smartphones.
- Ideal for remote workforces as users can access virtual desktops from any device
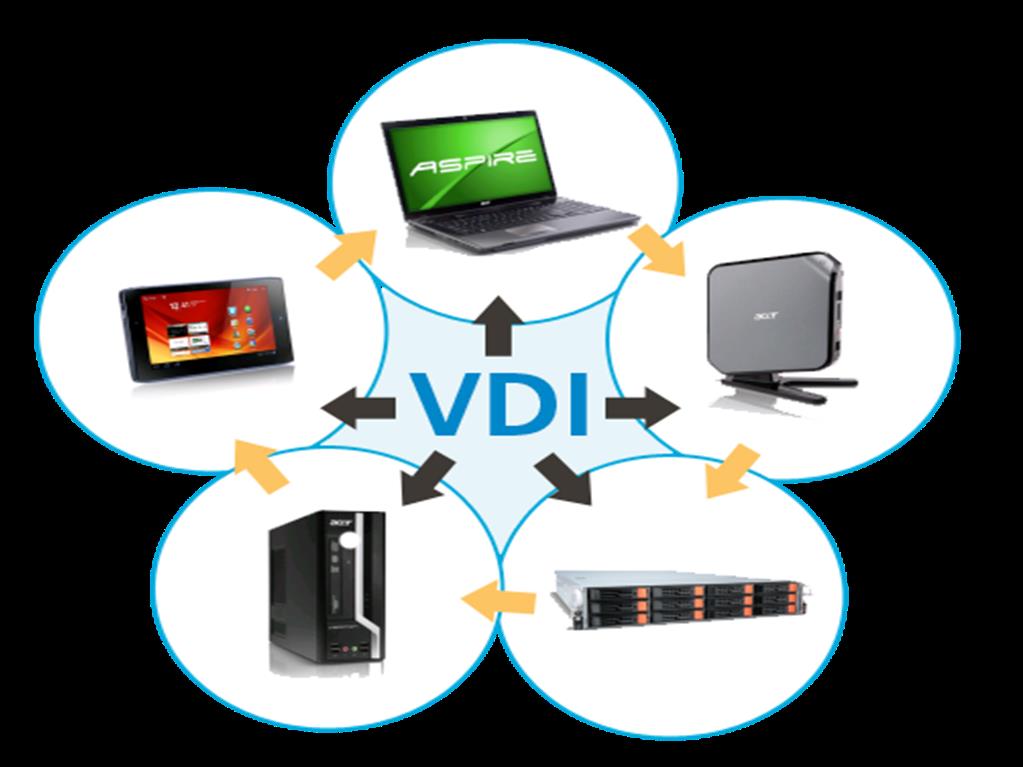
Challenges of VDI
While VDI offers enhanced security and flexibility, it presents challenges, primarily due to its complex infrastructure setup and maintenance requirements. VDI demands significant investment in servers, storage, and networking equipment, which can be time-consuming and often require skilled IT professionals to manage. Performance issues may also arise, particularly if the network is not optimized for heavy traffic. High user numbers can lead to slow performance and latency, frustrating users and lowering productivity. Additionally, scaling VDI can be expensive, as more powerful hardware is needed to accommodate an increasing number of users.
What is RDP?
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a Microsoft protocol that allows users to remotely connect to and control another computer or server, mimicking physical presence. Widely used for remote work, server management, and troubleshooting, RDP is built into most Windows versions, making it easily accessible. It enables IT administrators to manage systems across multiple locations without physical access. RDP transmits commands and the graphical interface between the client and the remote machine in real time, using encryption for secure communication. With a stable internet connection, RDP offers a seamless, low-latency experience.
Advantages of RDP for Remote Work
- Ease of use: Built into most versions of Windows, requiring no additional software installation.
- Cost-effective solution for organizations of all sizes.
- Flexibility: Allows users to access desktops and applications from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Ideal for remote workers needing access to company resources from various locations.
- Provides full administrative control over the remote machine.
- Useful for IT professionals managing servers and troubleshooting remotely.
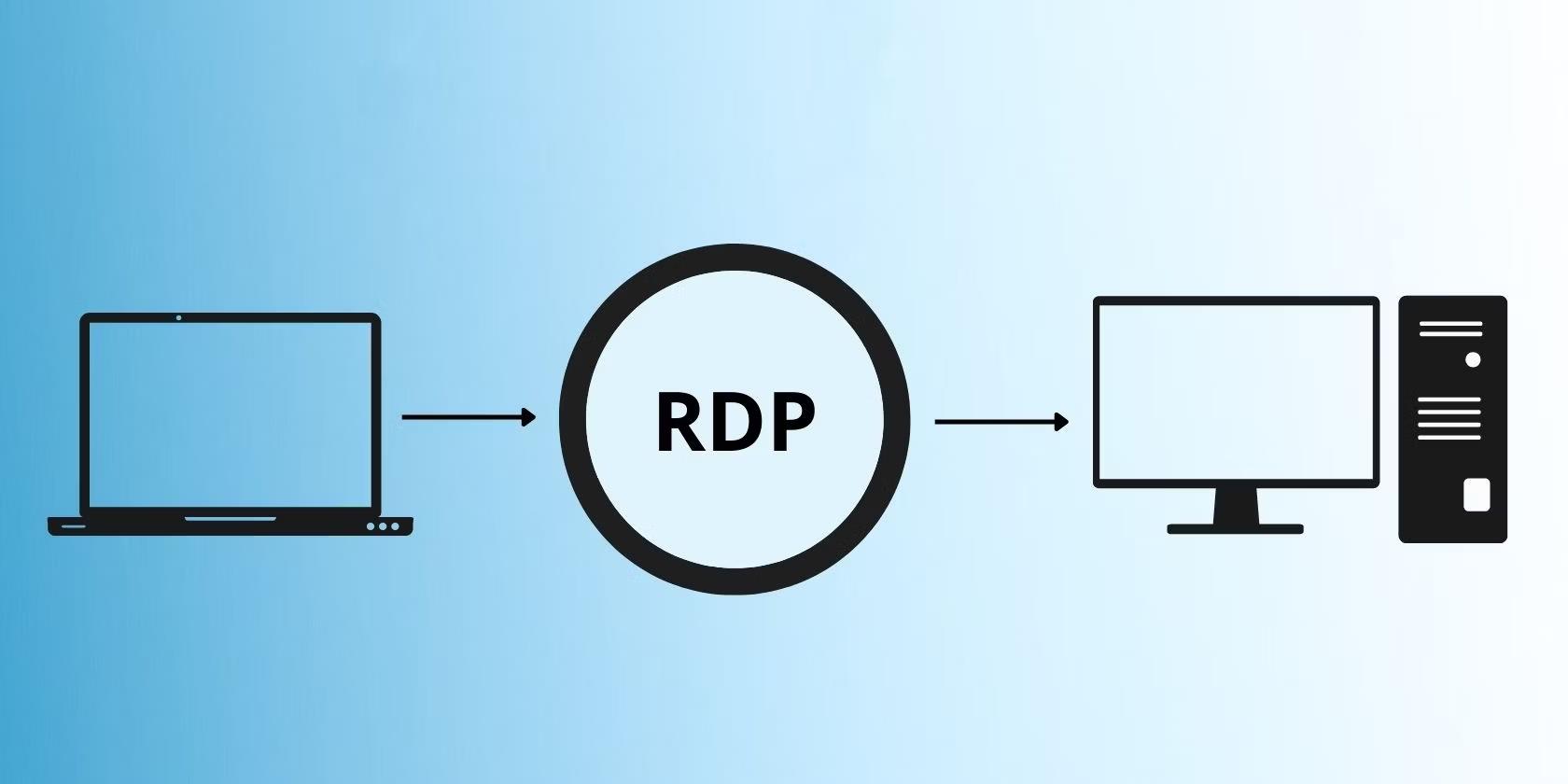
Limitations of RDP
Despite its benefits, RDP comes with notable limitations, primarily its dependence on a high-speed, stable internet connection. Slow or unreliable connections can lead to lag, making remote work frustrating and less productive, especially in areas with poor internet infrastructure. Additionally, RDP is optimized for Windows environments, and although it can work with other operating systems, the setup is more complex, and the user experience may not be as smooth. Full access to the remote machine also poses security risks if not properly configured, making robust security measures like firewalls and two-factor authentication essential.
What is RDS?
Remote Desktop Services (RDS) allows multiple users to share a single Windows server, providing access to applications and desktops. Unlike VDI, which provides individual virtual machines, RDS centralizes resources, making it more efficient and cost-effective. It’s ideal for environments where users need the same software, such as accounting or office applications, and reduces hardware expenses. RDS simplifies remote access by allowing users to connect from any device, with computing handled on the server. This centralized management also makes it easier for IT administrators to handle updates and security, offering a streamlined remote access solution.
Key Benefits of RDS
- Cost-efficiency due to multiple users sharing the same server.
- Reduces hardware costs by avoiding the need for separate machines for each user.
- Lowers energy consumption and maintenance efforts.
- Simplifies software license and update management, saving time and resources for IT departments.
- Enhances security by storing data on the server instead of user devices, minimizing data loss risks.
- Centralized security measures like firewalls and encryption can be implemented.
- Protects sensitive data, even when accessed remotely.
- Scalable and secure solution suitable for organizations of all sizes.

VDI vs. RDP vs. RDS: What Are the Differences?
VDI, RDP, and RDS are three different remote access solutions that cater to various organizational needs. While they all provide remote access, their structure, usage, and associated costs vary significantly. Each option offers distinct benefits and challenges depending on factors like operating system compatibility, scalability, and ease of administration. Here’s a breakdown of the key differences:
- Operating System Compatibility: VDI offers flexibility across Windows, macOS, and Linux, making it ideal for diverse environments. RDP works primarily with Windows but can be configured for macOS and Linux. RDS is mostly restricted to Windows Server.
- Number of Servers Required: VDI requires a separate server per virtual machine, increasing costs. RDP and RDS need fewer servers, with RDP working on a single machine and RDS allowing resource sharing among users.
- Scalability and Flexibility: RDP and RDS are more scalable as they allow multiple users to share resources without additional hardware. VDI requires more infrastructure investment to scale, making it more challenging for smaller organizations.
- Ease of Administration: RDP and RDS are easier to manage, with minimal setup for RDP and centralized user management in RDS. VDI’s complexity in setting up and maintaining virtual machines makes it harder to administer, especially for smaller organizations.
- Resource Allocation and Efficiency: VDI excels in resource allocation, providing dedicated CPU, memory, and storage for each user. RDP and RDS share server resources, which can lead to performance issues in high-demand situations.
- Desktop Customization Options: VDI allows extensive desktop customization, enabling users to tailor their virtual desktops. RDP and RDS offer limited customization with standardized desktop environments.
- Internet Connectivity Requirements: VDI offers some offline functionality, syncing data when the connection is restored, making it more resilient in areas with unreliable internet. RDP and RDS require a stable, always-on connection to function effectively.
- Overall Cost Comparison: RDP and RDS are more cost-effective, with RDP built into Windows and RDS reducing hardware costs by sharing resources. VDI, while offering more customization and security, requires a higher investment in hardware and software.
VDI vs. RDP vs. RDS: Similarities
VDI, RDP, and RDS share core similarities in providing remote access to computing resources, enabling flexible work environments. All three technologies allow users to connect to desktops or applications hosted on a central server, making remote work possible without the need for physical office presence. This flexibility helps businesses maintain productivity regardless of where employees are working. Additionally, they reduce the need for high-end hardware for every user, centralizing computing power on servers, which streamlines IT management and reduces overall costs.
- User Experience Across Platforms: VDI, RDP, and RDS all offer reliable remote access, ensuring users can seamlessly access applications, files, and resources from multiple devices. These platforms provide a similar experience to local desktops, with stable internet ensuring minimal lag. While they all share common features, each solution has its strengths depending on the organization’s specific needs.
- Security and Data Protection: All three solutions store data on centralized servers, reducing security risks. They use encryption and security measures like firewalls and multi-factor authentication to ensure sensitive data is well protected.
- Choosing VDI for Complex Environments: VDI is ideal for businesses needing high customization and security. Each user gets a dedicated virtual machine, which is perfect for industries requiring specialized configurations, such as software development or research.
- Why RDP Might Be Enough for Most Users: RDP is built into most Windows systems, making it an easy, cost-effective option for small businesses. It provides basic remote access without needing additional software or hardware, meeting most users’ needs.
- When to Choose RDS for Your Organization: RDS centralizes resources on a shared server, reducing hardware costs and making it ideal for organizations where multiple users need access to the same applications. It’s efficient, low-maintenance, and easy to manage.
Conclusion
Choosing between VDI, RDP, and RDS depends on your organization’s specific needs. VDI is ideal for complex environments requiring high customization and security, while RDP provides a simple, affordable solution for smaller businesses. RDS strikes a balance between shared resources and ease of management, making it suitable for larger teams needing uniform access. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your goals, whether it’s customization, cost-efficiency, or management simplicity.







