
Lightweight Tools to Monitor and Secure Your Linux VPS
Running a Linux VPS gives you control, flexibility, and performance—but it also means you are responsible for keeping your system secure and optimized. Fortunately, you don’t need heavy enterprise software to monitor and protect your VPS. A combination of lightweight, command-line tools can efficiently perform the job without slowing down your server.
In this guide, we’ll explore 10 lightweight tools every VPS owner should know about. Each tool is resource-friendly, easy to use, and powerful enough to help you maintain security and performance.
—————————————-
1. htop – Real-Time Process and Resource Monitor
**Purpose:** htop is a visual, interactive process viewer and system monitor. It’s the modern, colorful alternative to the classic “top” command.
**Example usage:**
“`
sudo apt install htop
htop
“`
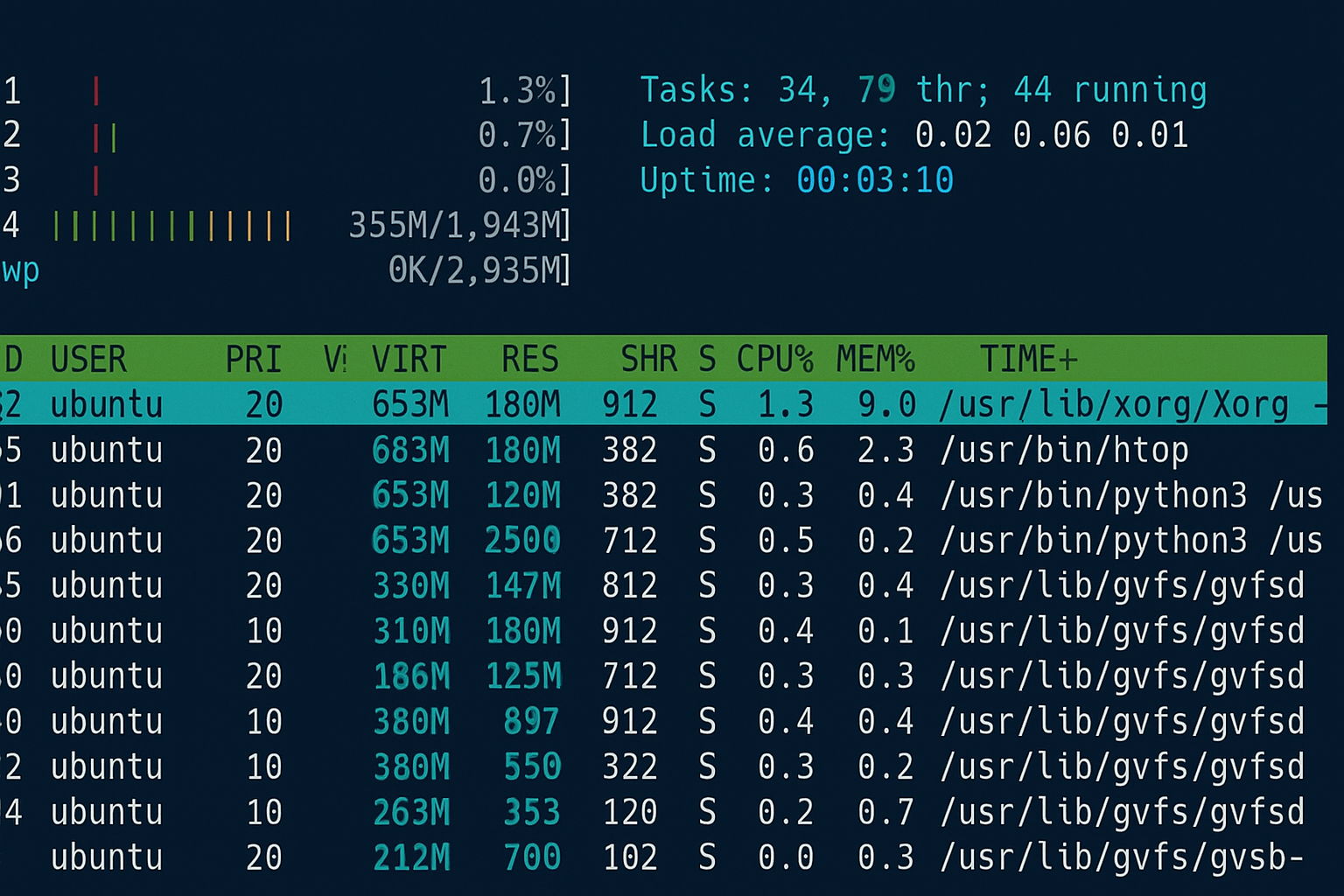
**Pros:**
– Clean, color-coded interface
– Let’s you kill or renice processes easily
– Lightweight and fast
**Cons:**
– Doesn’t display disk I/O statistics by default
– Lacks remote monitoring support
**Use case:** Ideal for quickly identifying resource-hungry processes on your VPS.
—————————————-
2. lsof – List Open Files and Network Connections
**Purpose:** lsof (List Open Files) shows which files and ports are currently being accessed by which processes. It’s an essential diagnostic tool for identifying abnormal network activity or open ports.
**Example usage:**
“`
sudo lsof -i
sudo lsof /var/log/syslog
“`
**Pros:**
– Great for investigating suspicious connections
– Helps detect locked or corrupted files
– Available by default on most systems
**Cons:**
– Output can be overwhelming without filters
**Use case:** Use it when you suspect a backdoor, or want to confirm which process is using a specific port.
—————————————-
3. Lynis – Security Auditing and Hardening Tool
**Purpose:** Lynis performs a full system audit, checking configuration files, permissions, and kernel settings to find security weaknesses.
**Example usage:**
“`
sudo apt install lynis
sudo lynis audit system
“`
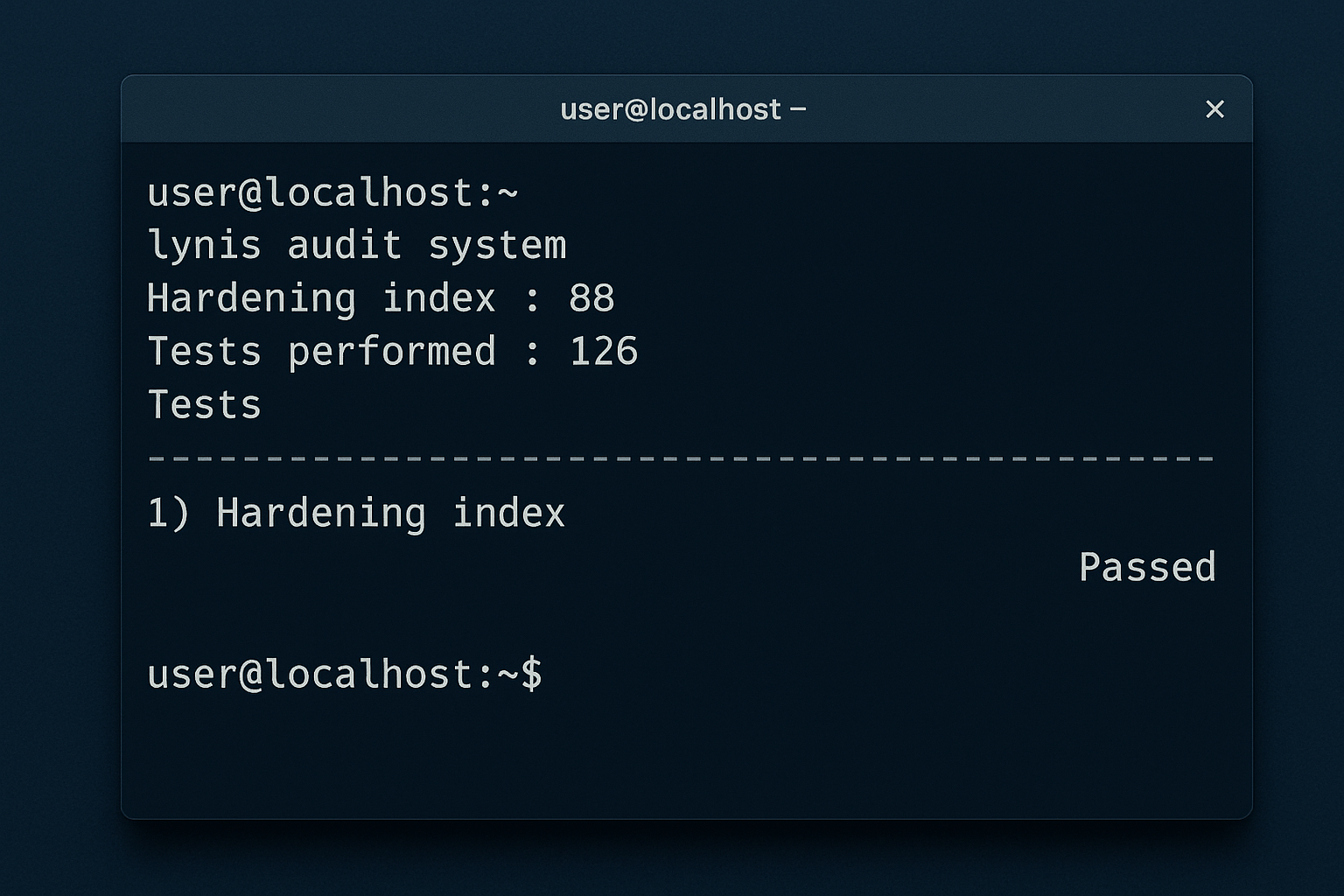
**Pros:**
– Comprehensive security scan
– Provides detailed recommendations for hardening
– Lightweight and non-intrusive
**Cons:**
– Reports require manual review and interpretation
**Use case:** Run Lynis after initial VPS setup and regularly after updates to ensure configurations remain secure.
—————————————-
4. Fail2ban – Brute-Force Attack Prevention
**Purpose:** Fail2ban scans log files for suspicious patterns (e.g., multiple failed login attempts) and bans offending IPs automatically.
**Example usage:**
“`
sudo apt install fail2ban
sudo systemctl enable --now fail2ban
“`
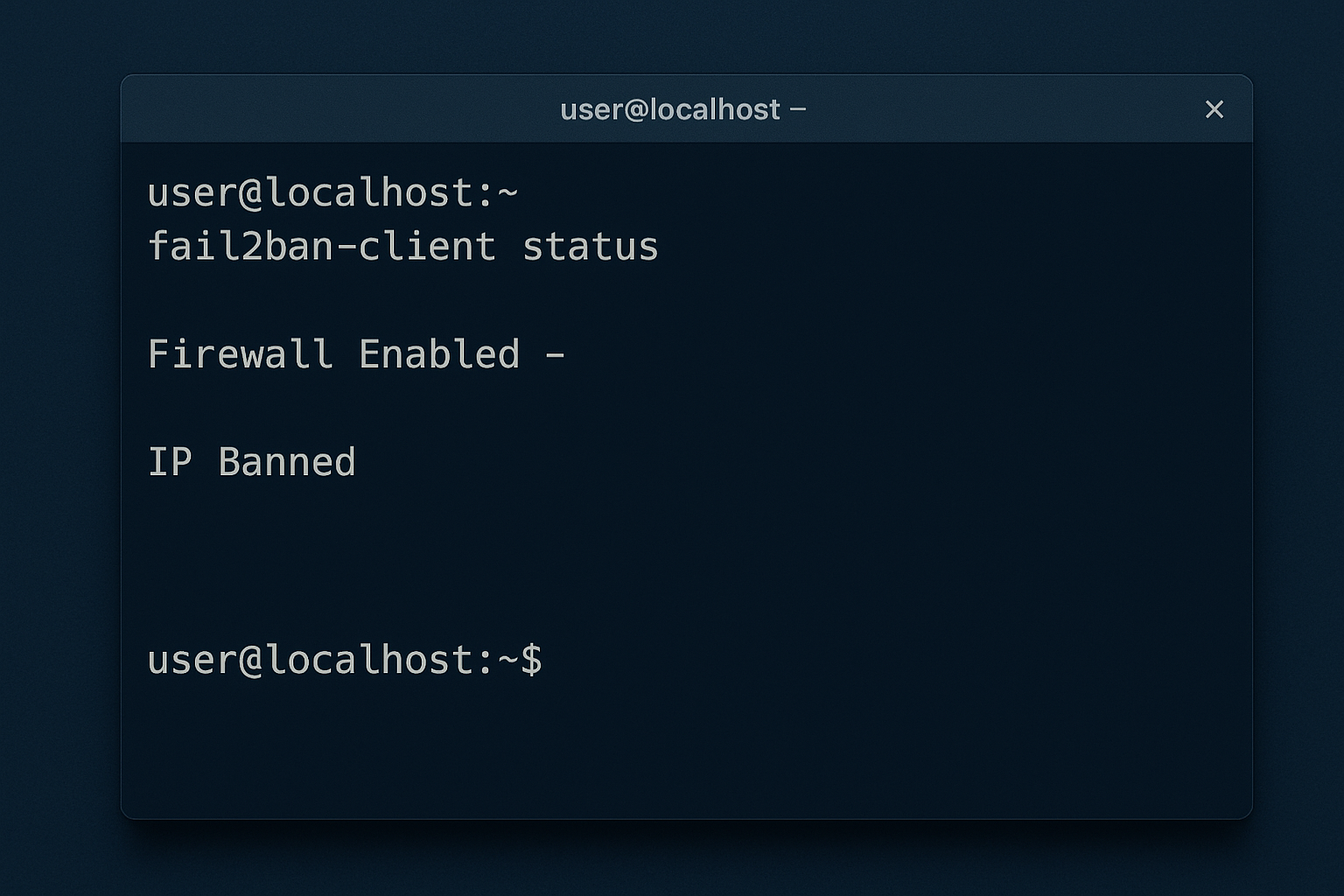
**Pros:**
– Protects SSH and web services automatically
– Customizable jail configurations
– Uses minimal system resources
**Cons:**
– Misconfiguration may accidentally block legitimate IPs
**Use case:** Essential for all public-facing VPS servers with SSH access.
—————————————-
5. UFW – Uncomplicated Firewall
**Purpose:** UFW provides a simple interface for managing iptables rules, helping users enable or disable ports easily.
**Example usage:**
“`
sudo apt install ufw
sudo ufw enable
sudo ufw allow 22/tcp
“`
**Pros:**
– Easy to use, even for beginners
– Perfect for small and medium VPS setups
– Logs blocked connections
**Cons:**
– Lacks advanced features like traffic shaping
**Use case:** Basic firewall protection for everyday VPS needs.
—————————————-
6. rkhunter – Rootkit and Backdoor Detection
**Purpose:** Rootkit Hunter scans for rootkits, backdoors, and malicious exploits on your VPS. It compares system binaries and looks for suspicious changes.
**Example usage:**
“`
sudo apt install rkhunter
sudo rkhunter --check
“`
**Pros:**
– Detects hidden and persistent threats
– Lightweight and easy to run
**Cons:**
– Can generate false positives
**Use case:** Schedule regular scans via cron for continuous protection.
—————————————-
7. iftop – Real-Time Network Bandwidth Monitoring
**Purpose:** Iftop displays active network connections and bandwidth usage in real time. It’s like htop but for network activity.
**Example usage:**
“`
sudo apt install iftop
sudo iftop
“`
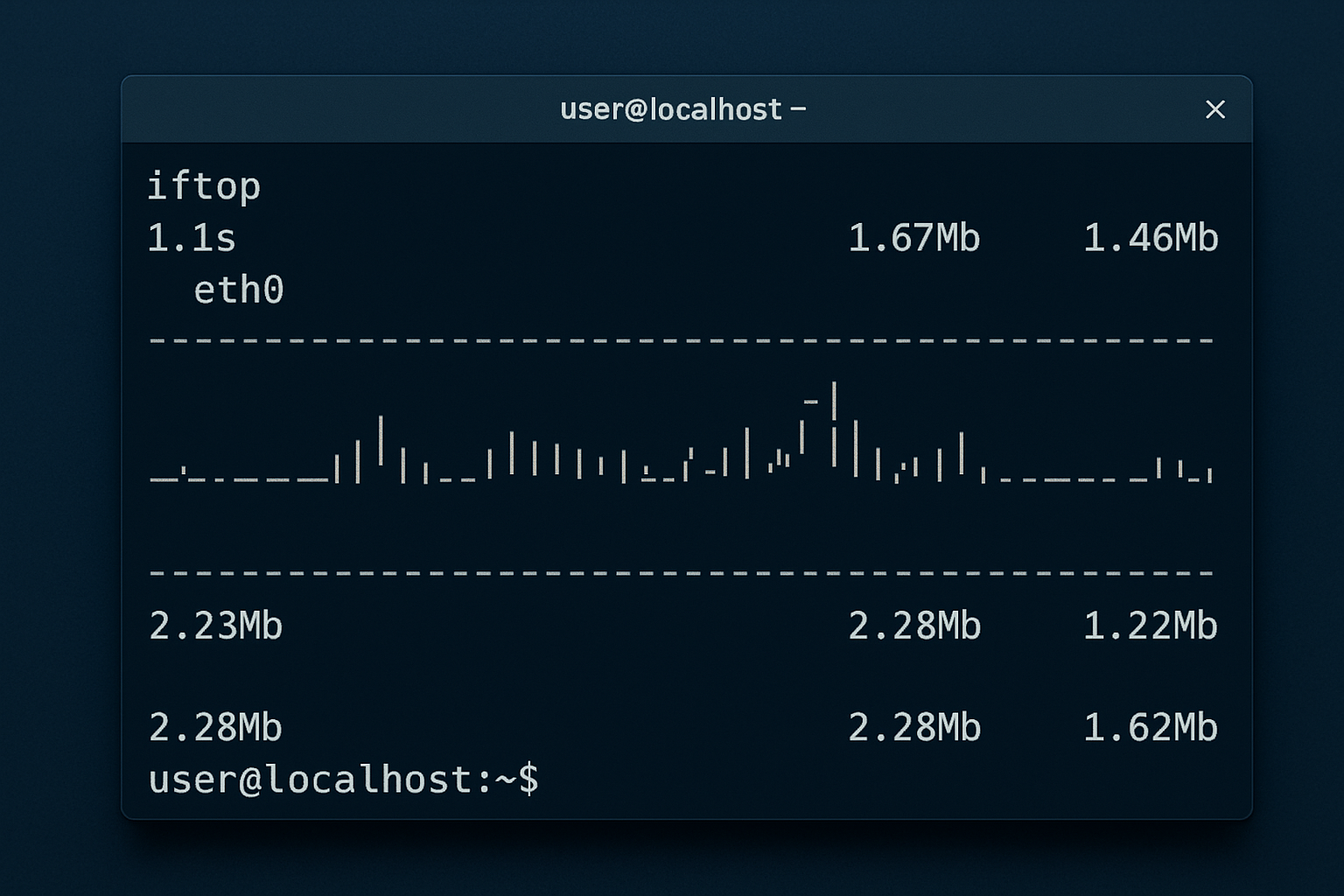
**Pros:**
– Real-time visualization of network traffic
– Detects unusual outbound activity quickly
– Very light on CPU usage
**Cons:**
– No built-in logging or historical data
**Use case:** Diagnose bandwidth spikes or suspicious outgoing traffic.
—————————————-
8. chkrootkit – Quick Rootkit Scanner
**Purpose:** chkrootkit searches for known rootkits and system modifications that may indicate compromise.
**Example usage:**
“`
sudo apt install chkrootkit
sudo chkrootkit
“`
**Pros:**
– High-speed scans
– Works on nearly all Linux distributions
**Cons:**
– Limited detection for newer or customized rootkits
**Use case:** Quick integrity check after major updates or system compromises.
—————————————-
9. ss / netstat – Monitor Active Network Connections
**Purpose:** These tools display sockets, ports, and network connections. ss is the modern replacement for netstat and runs faster with less overhead.
**Example usage:**
“`
sudo ss -tuln
“`
**Pros:**
– Built into most Linux systems
– Ideal for network debugging
– Very low resource consumption
**Cons:**
– Output is text-only (no visualization)
**Use case:** Check for unexpected open ports or active connections.
—————————————-
10. logwatch – Automated Log Analysis
**Purpose:** logwatch parses system logs and generates daily summaries about activities, errors, and potential issues.
**Example usage:**
“`
sudo apt install logwatch
sudo logwatch --detail high --service all
“`
**Pros:**
– Sends daily email reports
– Great for early anomaly detection
– Easy to configure
**Cons:**
– Requires tuning to reduce noise
**Use case:** Keep daily visibility over your VPS’s health and security.
—————————————-
Extra Tips for VPS Hardening
In addition to using these tools, you can improve your VPS security with the following best practices:
1. Regularly update your packages and kernel.
2. Disable root SSH login and use a regular user with sudo privileges.
3. Set up SSH key authentication instead of passwords.
4. Limit open ports and close unused services.
5. Use secure protocols such as HTTPS, SFTP, and TLS whenever possible.
6. Perform regular backups and store them safely.
7. Monitor system logs frequently to identify unusual behaviour early.
8. Consider intrusion detection tools like OSSEC or AIDE for advanced setups.
—————————————-
Conclusion
Lightweight monitoring and security tools can help you maintain your Linux VPS efficiently without consuming excessive resources. Whether you’re running a small website or managing multiple virtual servers, these tools provide transparency, control, and protection against common threats.
You don’t need a massive security suite—just the right combination of open-source utilities. Tools like htop, Lynis, Fail2ban, and UFW can keep your VPS running smoothly and securely.
👉 Order your VPS now and secure it efficiently.

